Our Editors-in-Chief’s Top Picks
The Editors-in-Chief of our CASS publications have selected some noteworthy papers from the recent issues of our journals:
IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers
Paper 1:
S. Moriya et al., "Analog VLSI Implementation of Subthreshold Spiking Neural Networks and Its Application to Reservoir Computing," IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, vol. 72, no. 10, pp. 5571-5582, Oct. 2025, doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2025.3550876. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10937735
Summary: For the sustainable advancement of AI in the coming decade, energy-efficient hardware will be indispensable. This research unveils a brain-inspired (neuromorphic) chip featuring fully analog spiking neural networks. By exploiting the extremely low-voltage operation of transistors in the subthreshold region, the system achieved an ultra-low power consumption of just a few tens of femtojoules for essential operations of spiking neuron. A multi-chip system successfully processed time-series data, demonstrating 81% accuracy in spoken digit recognition. This innovation provides crucial insights for edge AI applications and could enable battery-less sensor systems powered entirely by energy harvesting.
Paper 2:
Z. Zhang et al., "Programmable Analog-to-Digital Converter Array Supporting Architecture Restructuring and Mode Concurrency,” IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, vol. 72, no. 10, pp. 5351-5364, Oct. 2025, doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2025.3533539. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10864395
Summary: Researchers at Tsinghua University have introduced a Programmable Converter Array (PCA) that redefines how ADCs adapt to diverse baseband signals. Unlike conventional ADCs fixed to a single specification or multi-mode ADCs limited by circuit switching, the PCA enables architectural reconfiguration and mode concurrency. Each unit, called a Conversion Block, can work independently or be combined to realize architectures including SAR, Pipe SAR, NS-SAR, TI-SAR, and other hybrids. Fabricated in 28nm CMOS, the prototype supports over 16 configurations, achieving an SNDR of 30 to 80 dB and bandwidths from sub-MHz to 1 GHz. It demonstrates unprecedented flexibility and performance in reconfigurable ADCs.
IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs
Paper 1:
N. Ginzberg and E. Cohen, “A Voltage-Mode I/Q Switched-Capacitor Doherty Power Amplifier With Dynamic Core Scaling for Enhanced Backoff Effciency,” IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, vol. 72, no. 11, pp. 1720 - 1724, Nov. 2025. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2025.3607681. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/11153981
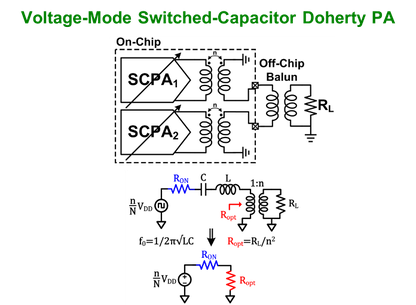
Summary: Modern wireless transmitters often operate below maximum power to maintain linearity, which reduces power amplifier efficiency. This work presents a digital voltage mode switched capacitor Doherty power amplifier with dynamic core scaling. The core is intentionally oversized to increase peak power, and at backoff the effective core size is reduced to obtain efficiency peaking by placing selected unit cells in Hi-Z. The Hi-Z logic prevents disconnected capacitors from floating, preserving capacitance ratios, matching, and linearity. A 65 nm CMOS prototype reaches 32% peak system efficiency at 25 dBm output power around 2.5 GHz, with a 3 dB operational bandwidth of 1.7 to 2.8 GHz. Compared to a Class-B PA, system efficiency improves by 1.3× at 3 dB backoff and 1.83× at 7 dB backoff. It also achieves −37 dB EVM at 14 dBm average output power for a 20 MHz OFDM Wi-Fi signal using piecewise digital predistortion.
Paper 2:
Z. Li et al., "A 3.4-GS/s 12-Bit Time-Interleaved Pipelined SAR ADC With Non-Foster Ring Amplifier-Based High-Linearity Track-and-Hold Amplifier," IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, vol. 72, no. 10, pp. 1348-1352, Oct. 2025, doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2025.3595185. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/11111691
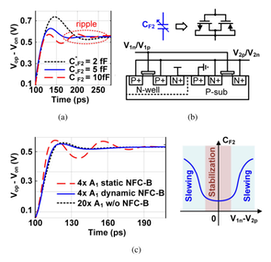
Summary: This work presents a 3.4-GS/s 12-bit time-interleaved pipelined SAR ADC fabricated in 28-nm CMOS, incorporating a high-linearity track-and-hold amplifier (THA) based on the proposed non-Foster ring amplifier (NFRA). By leveraging inter-stage delay reduction and feedback factor compensation based on non-Foster capacitors (NFCs), the proposed NFRA enables fast and stable settling while preserving high linearity, effectively overcoming the stability limitations of conventional ring amplifiers (RingAmps). The prototype ADC achieves 57.3-dB SNDR and 77.6-dB SFDR at near-Nyquist input, while maintaining 53-dB SNDR and 73.2-dB SFDR up to 3.5 GHz with a total power consumption of 92 mW.
Paper 3:
B. Veraverbeke and F. Tavernier, "A Cryo-CMOS Triple Tail Comparator With Capacitive Over-Neutralization to Suppress Freeze-Out Induced Hysteresis," IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, vol. 72, no. 10, pp. 1358-1362, Oct. 2025, doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2025.3596708. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/11119638

Summary: Why is it so difficult to build a quantum computer? Besides intricate quantum mechanical issues, it is challenging to implement classical electronics to interact with the quantum bits. To facilitate large-scale quantum computing, these electronics should operate at cryogenic temperatures. Modern CMOS transistors are still functional at temperatures down to only a few millikelvin, but their cryogenic behavior is not yet fully understood, so that cryogenic anomalies complicate circuit design. This work provides additional insights into cryogenic CMOS behavior in three ways. Firstly, it describes how dopant freeze-out introduces hysteresis in cryogenic comparators. Secondly, a statistical hysteresis characterization procedure is developed. Finally, a triple tail comparator with capacitive over-neutralization is proposed to suppress the freeze-out induced hysteresis >6×.
IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technologies
Paper 1:
H. Ho-Ching Iu, U. Erkan, C. Simsek, A. Toktas, Y. Cao, "A 3D Memristive Cubic Map With Dual Discrete Memristors: Design, Implementation, and Application in Image Encryption," IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, vol. 35, no. 8, pp. 7706-7718, Aug. 2025, doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2025.3545868.
This paper introduces a novel discrete chaotic system employing dual memristors, named the 3D memristive cubic map with dual discrete memristors (3D-MCM). The 3D-MCM system demonstrates richer and more intricate dynamical behaviors compared to its single-memristor counterparts, as verified through bifurcation diagrams, Lyapunov exponent spectra, and complexity analyses. Notably, the system exhibits coexisting attractors, substantially enhancing its dynamical complexity. Hardware implementation of the 3D-MCM attractors confirms its feasibility for industrial applications. To illustrate the system potential in encryption tasks, this study integrates the quaternary-based permutation and dynamic emanating diffusion (QPDED-IE) scheme with the 3D-MCM for image encryption. Experimental results demonstrate that the QPDED-IE scheme based on the 3D-MCM exhibits strong diffusion and confusion properties, effectively resisting cryptanalytic attacks

Paper 2:
X. Min, Y. Gao, Y. Cao, G. Zhai, W. Zhang, H. Sun, "Exploring Rich Subjective Quality Information for Image Quality Assessment in the Wild," in IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, vol. 35, no. 8, pp. 7778-7791, Aug. 2025, doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2025.3544659.
This paper propose a novel Image Quality Assessment (IQA) method named RichIQA to explore the rich subjective rating information beyond MOS to predict image quality in the wild. RichIQA is characterized by two novel designs: 1) a three-stage image quality prediction network, which exploits the powerful feature representation capability of the Convolutional vision Transformer (CvT) and mimics the short-term and long-term memory mechanisms of human brain; 2) a multi-label training strategy in which rich subjective quality information like MOS, SOS and DOS are concurrently used to train the quality prediction network. Powered by these two novel designs, RichIQA is able to predict the image quality in terms of a distribution, from which the mean image quality can be subsequently obtained. Experimental results verify that the three-stage network is tailored to predict rich quality information, while the multi-label training strategy can fully exploit the potentials within subjective quality rating and enhance the prediction performance and generalizability of the network. It is also shown RichIQA outperforms state-of-the-art competitors on multiple large-scale in the wild IQA databases with rich subjective rating labels

Paper 3:
Y. Xue, B. Zhong, G. Jin, T. Shen, L. Tan, N. Li, "AVLTrack: Dynamic Sparse Learning for Aerial Vision-Language Tracking," in IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, vol. 35, no. 8, pp. 7554-7567, Aug. 2025, doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2025.3549953.
This work presents a flexible framework for aerial vision-language tracking called AVLTrack. It consists of three key components, a dynamic sparse learning (DSL) module, an efficient Transformer backbone, and a multi-level language perception (MLP) strategy. First, DSL sparsely connects language and images via dynamic sparse attention, providing accurate multi-modal prompts. To adapt to target state variations, the sparsity in DSL is dynamically adjusted based on semantic information, flexibly highlighting target-specific tokens. Next, the Transformer backbone follows highly parallelized one-stream architectures, allowing efficient multi-modal feature extraction and interaction. Finally, MLP enables the iterative interaction of language and visual information, aiming to utilize language priori to guide the generation of discriminative visual features. As an additional contribution of this work, the DTB70-NLP dataset is collected to facilitate UAV vision-language tracking. Experiments on WebUAV-3M and DTB70-NLP demonstrate the effective performance of AVLTrack compared to existing trackers, while maintaining a high running speed of 80.5 FPS. The dataset and codes are available at https://github.com/xyl-507/AVLTrack

IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems
Paper 1:
Das, S., Riedel, S., Naeim, M., Brunion, M., Bertuletti, M., Benini, L., Ryckaert, J., Myers, J., Biswas, D. and Milojevic, D., 2024. "Bandwidth-Latency-Thermal Co-Optimization of Interconnect-Dominated Many-Core 3D-IC," IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems. vol. 33, no. 2, pp. 346-357, Feb. 2025, doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2024.3467148 https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10720515
Summary: The article addresses the challenges faced by contemporary system-on-chips (SoCs) due to the increasing demands for memory bandwidth, capacity, and thermal stability, particularly in the context of advancing artificial intelligence (AI). It proposes architectural modifications for a many-core SoC designed to enhance on-chip cache memory bandwidth and optimize access latency. The SoC is fabricated using A10 nanosheet technology in a 3-D configuration, with thermal analyses conducted. Workload simulations demonstrate significant performance improvements, achieving up to 12-fold acceleration for a 64-core version and 2.5-fold for a 16-core version, accompanied by a 40% increase in die area and a 60% rise in power dissipation when using a 2-D design. In comparison, the 3-D design not only minimizes the physical footprint but also saves 20% in power consumption due to a 40% reduction in wirelength. The study emphasizes the importance of restructuring pipelines to optimize the benefits of 3-D technology for enhanced memory access and lower latency. Additionally, it explores thermal impacts of different 3-D partitioning approaches in high-performance computing (HPC) and mobile applications, finding that 3-D designs in mobile contexts only slightly increase maximum temperature (by about 2-3 °C) compared to 2-D, while HPC scenarios require careful partitioning strategies to effectively manage thermal constraints.
Paper 2:
G. Murali, M. Gyu Park and S. Kyu Lim, "3DNN-Xplorer: A Machine Learning Framework for Design Space Exploration of Heterogeneous 3-D DNN Accelerators," IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, vol. 33, no. 2, pp. 358-370, Feb. 2025, doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2024.3471496. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10715720
Summary: This paper introduces 3DNN-Xplorer, a novel machine learning (ML)-based framework for predicting the performance of heterogeneous 3-D deep neural network (DNN) accelerators. This framework enables design space exploration (DSE) of these accelerators with a two-tier compute-on-memory (CoM) configuration, considering 3-D physical design factors. The framework explores four distinct heterogeneous 3-D integration styles combining 28-nm and 16-nm technology nodes for both compute and memory tiers. Through extrapolation techniques and ML models trained on various accelerator configurations, the performance of larger systems is estimated, achieving a maximum absolute error of 13.9%. The framework considers area imbalance arising from different technology nodes by assuming equal numbers of PEs or on-chip memory capacity across integration styles. The analysis reveals that the heterogeneous 3-D style with 28-nm compute and 16-nm memory demonstrates energy-efficient performance, offering up to 50% energy savings and an 8.8% reduction in runtime compared to other 3-D integration styles. Conversely, the heterogeneous 3-D style with 16-nm compute and 28-nm memory proves area-efficient, exhibiting up to 8.3% runtime reduction compared to other 3-D styles.
Paper 3:
A. Almeida da Silva, L. Nogueira, A. Coelho, J. A. N. Silveira and C. Marcon, "Securet3d: An Adaptive, Secure, and Fault-Tolerant Aware Routing Algorithm for Vertically–Partially Connected 3D-NoC," IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, vol. 33, no. 1, pp. 275-287, Jan. 2025, doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2024.3500575 https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10766899
Summary: This article presents Securet3d, a novel routing algorithm designed for multiprocessor systems-on-chip (MPSoCs) that utilize 3-D networks-on-chip (3D-NoCs), aimed at enhancing secure and fault-tolerant operations. As MPSoCs play a crucial role in achieving effective parallel computing by sharing resources across complex applications, implementing adaptive mechanisms to safeguard sensitive data is essential. Securet3d builds upon the existing Reflect3d algorithm, introducing a comprehensive mapping scheme for secure data pathways and improving the system’s fault tolerance. The algorithm's effectiveness is validated through comparisons with three other fault-tolerant routing algorithms in vertically-partially connected 3D-NoCs. All algorithms were developed in SystemVerilog and evaluated via simulations using ModelSim, and hardware synthesis was performed with Cadence’s Genus tool. The experimental results indicate that Securet3d not only reduces latency but also enhances cost-effectiveness compared to other methods. Implemented with a 28-nm technology library, Securet3d exhibits minimal area and energy overhead, demonstrating its scalability and efficiency. Moreover, during denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, Securet3d maintains relatively stable average packet latencies of 70, 90, and 29 clock cycles for uniform random, bit-complement, and shuffle traffic, respectively, which are significantly lower than the latencies observed in other algorithms lacking security mechanisms (5763, 4632, and 3712 clock cycles on average). These findings underscore Securet3d's superior security, scalability, and adaptability for complex communication systems.
IEEE Journal on Emerging and Selected Topics in Circuits and Systems
Paper 1:
G. I. Haidar, J. Zhou, M. Sami Ul Islam Sami, M. M. Tehranipoor and F. Farahmandi, "SAFET-HI: Secure Authentication-Based Framework for Encrypted Testing in Heterogeneous Integration," IEEE Journal on Emerging and Selected Topics in Circuits and Systems, vol. 15, no. 3, pp. 478-492, Sept. 2025, doi: 10.1109/JETCAS.2025.3594675. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/11106505

Summary: The increasing reliance on untrusted outsourced test facilities exposes heterogeneous System-in-Package (SiP) designs to severe supply chain threats such as overproduction, IP theft, and reverse engineering. We propose SAFET-HI, a lightweight authenticated and encrypted testing protocol that integrates unique authentication, partial encryption, and designer-controlled unlock keys to maintain trust in the test process. Experimental validation shows that SAFET-HI ensures test integrity with minimal area (1.42–4.27%) and timing (13.7%) overhead, offering a scalable and practical defense framework for secure SiP testing.
Paper 2:
H. Yotsuyanagi, K. Takami and M. Hashizume, "An Implementation of Delay Testable Boundary Scan and Post-Bond Test Results in a 3D IC," IEEE Journal on Emerging and Selected Topics in Circuits and Systems, vol. 15, no. 3, pp. 469-477, Sept. 2025, doi: 10.1109/JETCAS.2025.3591617. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/11088072
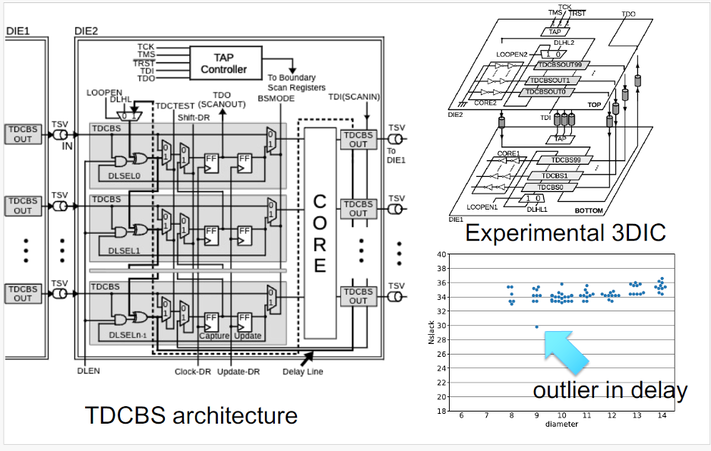
Summary: A defective through-silicon via (TSV) may cause a small delay fault that is difficult to detect using conventional logic testing methods. We have proposed a delay testable boundary scan design that has an embedded time-to-digital converter that can measure the timing slack between the test clock and an incoming signal through a TSV. This paper reports the results obtained for the first experimental 3D IC with this delay testable circuit and shows the possibility to detect a delay fault at a TSV interconnect.
Paper 3:
Y. -T. Yang and C. -M. Hung, "Heterogeneous Integration in Co-Packaged Optics," IEEE Journal on Emerging and Selected Topics in Circuits and Systems, vol. 15, no. 3, pp. 427-437, Sept. 2025, doi: 10.1109/JETCAS.2025.3590744.https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/11087222
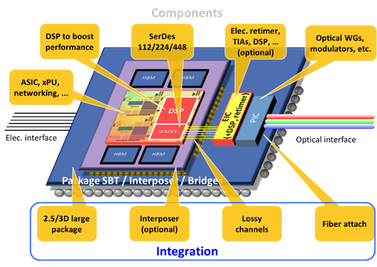
Summary: Generative artificial intelligence requires data centers to have higher bandwidth, and better energy efficiency. Co-packaged optics (CPO) is one of the future directions. In this paper, challenges in heterogeneous integration in CPO technologies are reviewed with two multi-physics packaging examples and corresponding mitigation methods are provided, including
(1) thermal crosstalk within the electrical domain and between the electrical and the optical interaction,
(2) SIPI of wide-and-slow and narrow-and-fast channel links,
(3) pros and cons of interposer material,
(4) photonics with light sources, optical coupling strategies, fiber attach schemes with advanced packaging, and integrated optical technologies.
IEEE Open Journal of Circuits and Systems
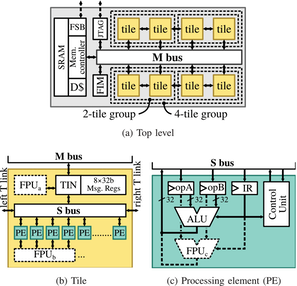
Paper 1:
T. Kaiser, E. Gottschalk, K. Biethahn and F. Gerfers, "Pasithea-1: An Energy-Efficient Sequential Reconfigurable Array With CPU-Like Programmability," IEEE Open Journal of Circuits and Systems, vol. 6, pp. 1-13, 2025, doi: 10.1109/OJCAS.2024.3518110. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10802954
Summary: This work presents Pasithea-1, a coarse-grained reconfigurable array (CGRA) that combines energy efficiency with CPU-like programmability.
Paper 2:
B. Yang, T. Caldwell and A. Chan Carusone, "An Energy-Efficient Pipeline-SAR ADC Using Linearized Dynamic Amplifiers and Input Buffer in 22nm FDSOI," IEEE Open Journal of Circuits and Systems, vol. 6, pp. 50-62, 2025, doi: 10.1109/OJCAS.2024.3509746. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10774063
Summary: This work presents a dynamic amplifier that achieves −52 dB in total harmonic distortion through an analog technique by which the expanding and compressing nonlinearities in the input transistors cancel one another. A pipeline-SAR analog-to-digital converter incorporating the linearized dynamic amplifier in both the input buffer and the first residue amplifier stage was designed and fabricated using the GlobalFoundries 22nm fully depleted silicon-on-insulator process.
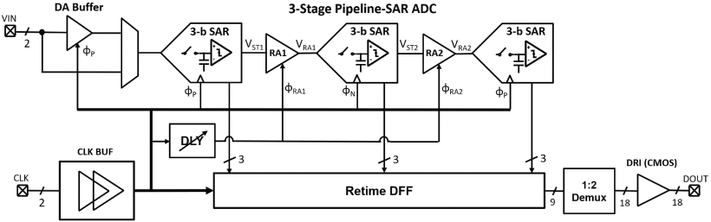
Paper 3:
S. Nowshin Chowdhury, M. Chen and S. Shah, "Analysis and Verilog-A Modeling of Floating-Gate Transistors," IEEE Open Journal of Circuits and Systems, vol. 6, pp. 63-73, 2025, doi: 10.1109/OJCAS.2024.3524363. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10818976
Summary: This work presents a Verilog-A model based on empirical measurements for a floating-gate transistor fabricated using a 65 nm CMOS process.
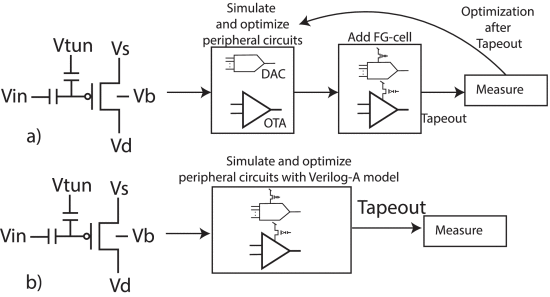
________________
IEEE CAS Magazine Third Quarter Issue 2025

Now available: Third Quarter Issue
IEEE Circuits and Systems (CAS) Magazine publishes original review articles and other articles that are of broad interest to the Circuits and Systems Society community. Interested authors are invited to send a three to four page White Paper first to the Editor-in-Chief, Prof. Keshab K. Parhi, by email here. If invited, they can submit a Full Paper at the Author Portal at the link below. CAS Magazine will continue to publish articles related to CAS Society Outreach. In addition, CAS Magazine also publishes articles related to education (such as tricks in solving problems and short lecture notes), conference highlights, chapter highlights, applications, and standards. Please feel free to submit articles that are of broad interest to the members of the CAS Society. For more information, please visit the IEEE Circuits and Systems Magazine on the CASS website.
________________
IEEE Transactions on AgriFood Electronics (TAFE) Special Issue on Autonomous Robotic Systems in Challenging Agricultural Settings

________________
Active "Call for Papers” Archive
______________________________
Latest Tables of Contents of CAS Sponsored Journals
The latest issues of our CAS sponored journals have been published and the tables of contents can be accessed through the following links:

- IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers
- IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs
- IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology
- IEEE Journal on Emerging and Selected Topics in Circuits and Systems
- IEEE Circuits and Systems Magazine
- IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems
- IEEE Design and Test Magaz
